Rubella is a viral infection, primarily affecting the skin and neck glands. This condition is caused because of Rubella virus. Rubella infection is generally considered mild in children, but can have serious consequences if it affects pregnant women.
Rubella Symptoms in Children
Children affected with rubella mostly experience a mild sickness. They may not exhibit any signs of being infected, but at the same time, they can pass on the infection to others. The very first noticeable symptom is pink or red rash on the face. These spots spread from the face towards the lower body. Some other signs that indicate rubella infection include
- Swollen and tender glands on the neck and at the back of ears
- Mild fever
- Mild body pains.
- Headache
- Red, puffy, burning eyes
- Cough
- Cold with runny nose
- Inflammation of nerves

How it affects Different Age Groups
Rubella can infect any person at any age. Symptoms can be seen after fourteen to 21 days. Most people may not show any signs of infection and may not be aware of being infected, but can become potential carriers of the virus and spread it to anyone who comes in contact with them. This rash resembles measles, but starts to fade away after three days on its own in children, without causing other health issues. But its effects vary in teenagers and adults. Joint aches are prominent and are more commonly observed in young women. Rubella is not a common occurrence in infants and adults over 40 years. If older people get infected, their symptoms can be more severe.
Rubella in Pregnancy
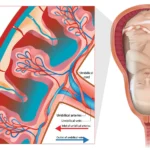
Rubella is a serious condition in pregnant women as it can affect the growing baby. It is important for everyone to get vaccinated. Otherwise they are stand a risk of being infected with Rubella. Even though Rubella has been eradicated from the U.S., there are still chances of being infected when travelling abroad or through visitors from other nations.
Women must take precautionary measures to be safe from Rubella before and during pregnancy. You should get vaccinated if you are planning for a baby before itself, because vaccine cannot be administered during pregnancy period. If the expecting mother is infected, it can result in severe health complications in babies. Rubella infection in pregnancy is most likely to occur in the first trimester and there is 90% probability of this virus spreading to the fetus around this time.
Vaccination is the only form of prevention against rubella virus, because it has no specific treatment method. Children born to mothers with rubella during pregnancy, may suffer from congenital rubella syndrome which can cause permanent health damage.