Rubella, also known as German measles is an infection caused by the virus Rubella. It is usually not a serious condition in most people, but poses serious threats if you are expecting.
Symptoms
Persons infected with rubella usually have a mild increase in body temperature. They may also have cough and cold. One important sign to distinguish rubella is the appearance of red or pinkish rash, that starts on a person’s face and later spreads to the lower body. There is also inflammation of neck glands and tenderness in those areas.
The symptoms may last for three days and then the pinkish red spots start to fade away on their own, leaving an itchy sensation in the affected areas. This condition is mostly seen in children, but usually doesn’t cause much harm to their health. Since the symptoms are often mild, people who are infected, may not realise the presence of this disease. Only a blood test prescribed by the doctor can diagnose the disease. Those infected can spread it to others unknowingly.

How it Spreads?
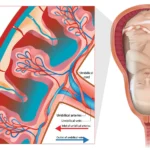
You may catch rubella when you come in close contact with infected people. Droplets from coughing or sneezing can pass on the infection to others. Pregnant women can pass on the rubella virus to their growing fetus in the womb. The infection can happen during the pregnancy period or during labor. Depending on when the infection arises and spreads to the fetus during pregnancy, there is a possibility of different health consequences.
Complications of Rubella During Pregnancy
- If the infection occurs during the first trimester and spreads to the fetus, the baby is most likely to be affected with long term health issues.
- In case the infection happens during the second trimester, within 20 weeks of being pregnant, the virus spreads to the developing baby from the mother. This results in congenital rubella in babies when they are born. These infants likely remain contagious for a year and more.
- If the infection to the baby in the womb takes place during 12 to 20 weeks, the resulting health problems are much lower.
- If the infection occurs after 20 weeks, it is not likely to cause any problems to the fetus at this stage of pregnancy.
It is the first three months that are considered very risky, for the fetus to get infected during pregnancy. Affected babies born with Congenital Rubella Syndrome can have serious health complications including
- Hearing impairment
- Heart problems
- Slow improvement
- Diabetes
- Cataracts in the eyes
- Thyroid gland issues
- Damage to the liver and spleen
In certain cases, rubella in expecting women can lead to a miscarriage. Sometimes, the affected babies do not survive long after being born. It is most important for women to get vaccinated at least a month ahead, if they plan on getting pregnant. Vaccine cannot be given in case you are already expecting with the baby.
You should be aware that rubella has no specific treatment and vaccination is the best way to avoid it during pregnancy and pass it on to your baby.