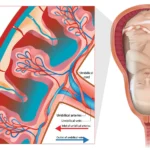
Chorioamnionitis is an infection that affects the womb in pregnant women. When this condition occurs, the membranes encompassing the fetus (chorion and amnion), the amniotic fluid and the umbilical cord get infected. This condition, also called as intrauterine infection, is caused by bacteria. This infection is common in expecting women and most of the times does not cause any harm to the mother or the baby.
How Chorioamnionitis Effects Pregnancy
Chorioamnionitis means both the expecting mother and the baby are infected. It disturbs the nutrient supply to the baby from the mother and requires the baby to be delivered soon. This means the baby is likely to be born premature. The fetus can also get infected during normal vaginal birth.
Even though you might be infected with chorioamnionitis when pregnant, it may not lead to any serious issues in most of the cases. However, if it is not managed timely, the infection can spread to the fetus and cause lifelong complications. When detected early, severe damage can be avoided by the doctors with the help of important precautionary measures. You may be prescribed with antibiotics to stop the infection and a timely caesarean birth may be required.

Causes of Chorioamnionitis
The bacteria that is responsible for this condition, is the generally occurring bacteria in most women on skin or vagina. This is usually harmless, but in certain cases, the bacteria may travel to other areas of the body and cause problems. Chorioamnionitis infection mostly occurs in the urinary tract of pregnant women. The infection first arises in the vagina or rectum and migrates to the womb. Bacteria may also move towards the uterus through the fallopian tubes, cervix or placenta. Anaerobes, E-Coli and Group B Streptococci are responsible for affecting pregnant with intrauterine infection.
Chorioamnionitis also occurs right before the onset of labor, when the water breaks. Other factors that pose a risk of this infection include preterm labor, prolonged labor, obesity, multiple vaginal tests, no previous births, urea plasma, use of hormones to induce labor, short cervix, use of epidural as anaesthetic, monitoring labor internally, smoking, drinking or drug abuse.
Symptoms of Chorioamnionitis
You should know that some pregnant women show no signs of infection at all. Some of the symptoms to look out for may include
- High fever
- Rapid heartbeat in mother and fetus
- Low blood pressure
- High count of white blood cells in the mother
- Tenderness of the uterus
- Sweating profusely
- Foul smelling vaginal fluid discharge
If you experience any of these signs and symptoms, you should consult your healthcare provider at the earliest and take necessary steps to prevent the spread of infection and to avoid future risks.