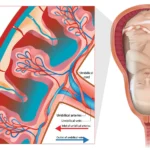
Pulmonary embolism or PE is the sudden blockage in the lung artery. Usually, this blockage is caused by a blood clot that travels to the lung from a vein in the leg. Most often, PE is a complication of the condition called as deep vein thrombosis. Most of these clots are small and are not deadly, but they can damage your lungs.
What causes a pulmonary embolism?
Blood clots are usually formed in the deep veins of the legs when there is restricted or slow blood flow. This condition can occur when you don’t move around for a longer period, such as:
- When you did a long trip in the airplane or car
- After undergoing some kinds of surgery
- Staying on the bed for extended periods
There is a great chance to develop the blood clots in the veins that are damaged from any injury or surgery. Also, some people have blood that clots too easily. There are some conditions that increase the chances of blood clotting, such as:
- Cancer treatments like radiotherapy and chemotherapy can increase the chances of blood clotting
- Heart failure
- Hughes syndrome, a condition in which blood becomes strangely sticky and increase the tendency to clot.
- Thrombophilia, which is an inherited condition that makes your blood more likely to clot.
There are various other risk factors that can increase the risk of PE, such as age, previous blood clots, obesity, pregnancy, smoking, family history and taking hormone therapy.

What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of PE can vary greatly, depending on how much of your lung is involved, clot size and your health condition. Most common symptoms include:
Chest pain: The pain is similar to a heart attack. The severity of pain increases when you a cough, eat, stoop, take deep breathe, or blend. Exertion will even worse the pain and it won’t go away even you take rest.
Shortness of breath: The symptom occurs suddenly irrespective of rest or active phase.
A cough: You may notice blood or blood-streaked mucus whenever you a cough.
Apart from the above symptoms, you may also notice symptoms like: excessive sweating, wheezing, fainting or lightheadedness, irregular or rapid heartbeat, swelling in the legs, and bluish-colored skin.
How to treat pulmonary embolism?
In case you are diagnosed with this condition, you need to get immediate treatment to avoid serious complications. If the condition is severe, you are prescribed with medications, such as anticoagulants and clot dissolvers that can dissolve blood clots.
During some conditions, other kinds of procedures are used, such as clot removal, vein filter, and surgery. If the clot is very large, it should be removed through the surgical procedure.