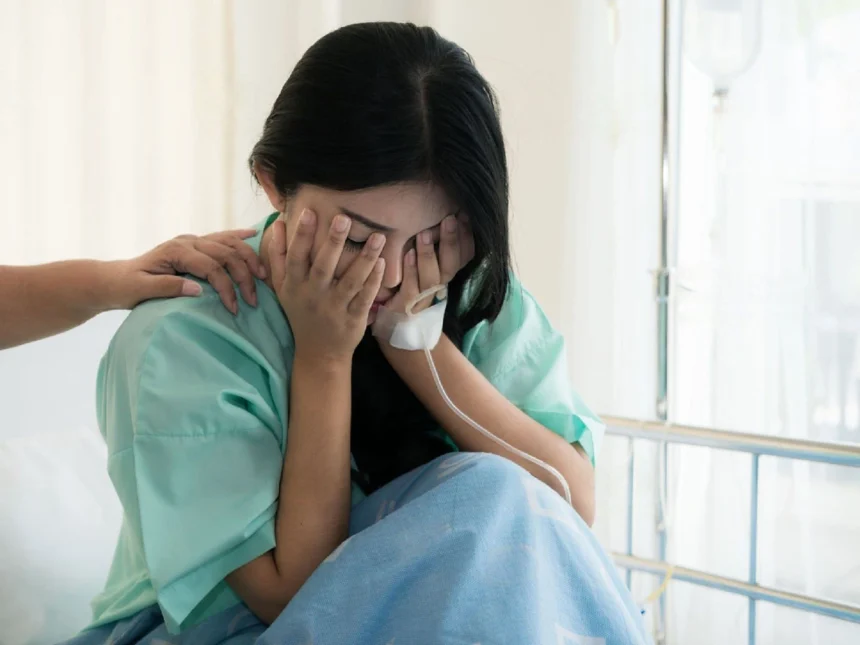
RPL is the short form of repeated pregnancy loss. This illness causes unquantifiable emotional trauma to family members as well as a profound sense of unworthiness in the mother. She continually fails to comprehend her vision of delivering an adorable and healthy baby, which is estimated to occur between 1% and 3% of all pregnancies. RPL is extremely difficult to treat. RPL is also known as habitual abortion and recurrent miscarriage. The following are the very common causative factors of RPL.
- Difficulties pertained to the uterus.
- Immunologic reasons
- Causes of endocrine dysfunction
- Genetic disorders
- Environmental provokes thrombophilia
- Infectious diseases
There exist numerous causative factors for recurrent pregnancy loss. Currently, there is a significantly less range of accepted causative factors. In most cases, this RPL cause is unknown.
Now let us discuss the causes of Repeated Pregnancy Loss below.
Difficulties Pertained to the Uterus/ Uterine Abnormalities –
The bicornuate and uterine septum structural modifications on the growth and shape of the uterus during childbirth, and the uterine lining can become damaged and develop scar tissue as a result of nursing after operations, contraction and curettage techniques, or fibroid revocation. Long-term deformities include fibroids and polyps.
Immunologic Dysfunction –
This cause is less evident in the rise of RPL as well as It may be because the immune system is not working properly.
Genetically Thrombophilia –
Although a link is there across the previous termination of pregnancy and inherited irregularities on the blood clotting ripple have been proposed, no definite link has been established; clot formation in the arteries which nourish the placenta is thought to hinder the circulation across the uterus and placenta, leading to earlier termination pregnancy.
Factors of Genetic Origin –
Firstly pregnancy may also fail due to aneuploids of the embryos. maternity wear
Medical Conditions –
Pregnancy loss has linked to insulin resistance and hypo- or hyperthyroidism. Similarly, maternal vascular disease and high blood glucose levels lead to an increased risk of diabetes in diabetic women. Placental Growth Factor

Parents Chromosomal Abnormality –
For instance, around 5% of married people have a minimum of two miscarriages. A reciprocal transmission( 50%), Robertsonian translocation ( 25%), or Mosaicism (10%) is the most common chromosomal irregularities, along with chromosomal reversals or sporadic irregularities accounting for the remaining portion.
Antiphospholipid Syndrome (APS) –
Moreover, It’s associated with APS and antibodies. The RPL, commonly in the second trimester, seems to be the very constant attribute of APS. It is an autoimmune condition that results in recurrent miscarriages.
Diagnosis of Repeated Pregnancy Loss
- Blood test
- Ultrasound
- Genetic screening
- Hormone tests
- Hysterogram
- Endometrial biopsy
However the strategy for treating repeated pregnancy loss patients is to obtain a detailed history, evaluations, and a full assessment of previous abortions and therapies accompanied by a study. Second the therapy depends on the outcomes of a thorough assessment. Pregnancy week by week
Therapies for Repeated Pregnancy Loss
In addition there seem to be several efficient medications available, and the best treatment recommended will be based on the outcome of an extensive evaluation. Pregnant patients should be under supervision before they start their pregnancy. In some conditions, blood thinners, hormone supplements and dietary supplements are prescribed. Genetic testing, egg or sperm donation, or gestational surrogacy are all possible options.
Recurrent pregnancy loss has a massive psychological effect. Psychological assistance like frequent conversations and compassionate counseling is crucial to the successful assessment and treatment of agitated couples. A diagnosis of non-primary causative factors or a delay in therapy will not ensure proper treatment for this condition. Next, likewise, a fetal salvage rate of 60%–20% exists.
Finally, every patient should understand that various options exist for everyone and that we are here to provide you with the needed information. But it’s best to consult your health care practitioner and proceed with the treatment options.