Each woman’s menstrual cycle will be different, and everyone won’t ovulate simultaneously in their cycle. That said, if you have long cycles and irregular periods, you will ovulate late – which affects the likelihood of pregnancy.
In this blog post, let’s discuss the late ovulation symptoms, causes, and how to track late ovulation.
What Is Ovulation?
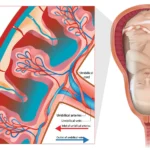
Ovulation typically happens between the 11-14th days of a menstrual cycle. During ovulation, a mature egg will release from an ovary. It occurs every month due to the rise and fall of certain hormones called estrogen, progesterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone.
What Are Causes Of Late Ovulation?
There are three phases in a menstrual cycle, which are –
- First Phase: The follicular phase starts on the first day of menstruation. During this phase, ovarian follicles develop, and an egg is prepared to release.
- Second Phase: Ovulation – when a mature egg released from an ovary moves into fallopian tubes.
- Third Phase: The luteal phase, in which the ruptured follicle closes and the lining of the uterus will shed if you don’t become pregnant.
The length of the luteal phase remains constant for all women, lasting around 14 days after ovulation, while the follicular phase may vary in size from 13-15 days. If you have a long follicular phase, your body takes more time to ovulate, in turn, late ovulation or absence.
Late ovulation is caused due to hormonal imbalances, which depend on your health condition. Here are a few factors that can trigger hormonal imbalance.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder that causes the ovaries to develop multiple follicles that appear as cysts. Due to raised levels of testosterone hormone, ovaries cannot release fully grown eggs. Women with PCOS tend to have irregular or prolonged periods and high male hormone levels.
Thyroid
The thyroid creates and produces hormones that regulate different systems in your body. You may have thyroid disease when your thyroid produces too much or very few hormones. Thyroid hormone imbalance can prevent ovulation.
Stress
Extreme stress is also one of the causes of hormonal imbalance and menstrual problems. Managing stress by doing activities can elevate this health condition.
Breastfeeding
When you are exclusively breastfeeding, your body naturally stops ovulation. However, your ovulation can return when you reduce or stop breastfeeding.
Medication
Certain medications can cause delayed or absent ovulation. Medications such as anti-inflammatories, antipsychotics, cocaine, marijuana, and anti-epileptic drugs can prevent the egg from being released.
What Are The Symptoms Of Late Ovulation?
For women with a 28-day menstrual cycle, ovulation occurs about day 14, although it may vary for some women. You can’t predict when it happens if you have irregular or delayed ovulation.
Here are a few symptoms to identify your ovulation time.
- Mild lower abdominal pain.
- Back pain.
- Increased cervical mucus.
- High basal body temperature.
- Breast soreness.
How To Track Late Ovulation?
Getting pregnant with late ovulation is possible as long as you ovulate. There are ovulation trackers and ovulation predictor kits, which help you know when your fertile window is open. However, you can also check your ovulation period through the signs and symptoms of ovulation.
If you want to get pregnant, talk with your doctor, and they will prescribe you medication that stimulates ovulation.
Bottom Line
Most women experience late ovulation these days. For some, it’s just temporary, and for some, it is caused due to some hormonal disorders.
Speak to your doctor about whether you have irregular or prolonged periods. Some treatments help in regulating ovulation and eliminate other health issues.