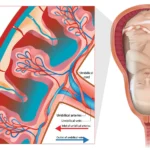
Vaginal thrush in pregnancy is a yeast infection caused by the Candida fungus. Most women experience fright. Thrush also occurs in pregnant women due to several body changes, but this condition is not a concern and can be easily controlled.
This infection usually arises in women because they wear fitted clothes or underwear. If you take antibiotics, you may also get this condition. Your body is subjected to rapid fluctuations in hormones during pregnancy. Increased estrogen production increases the possibility of developing vaginal thrush.
Medications can treat vaginal thrush in pregnancy, but you should not try to treat yourself when expecting.
Thrush in pregnancy
The bacteria usually stays in the vagina, where the usual vaginal bacteria keep it from growing. When the balance is disturbed by the hormones or stress, this fungus can increase, and you will have a white, semi-thick discharge with no smell. The fungus can make your vagina itchy and cause redness. You might experience burning while urinating or having sex.

However, you should know that this infection does not affect your pregnancy or baby in any way. If you are trying to get pregnant, having thrush does not lower your chances of having a baby. The thrush infection can affect your baby more than it usually does. Your doctor may prescribe a cream or tablets that can be inserted into the vagina to treat thrush.
Remedies to avoid and treat thrush
Simple preventive measures can prevent this yeast infection in pregnancy.
- Wear comfortable, loose, preferably cotton clothes and cotton underwear.
- Maintaining good hygiene is necessary, but avoid using personal hygiene products unless your doctor advises. These can do more harm than good.
- Avoid using products made from harsh chemicals, as these can cause skin irritation.
- You should avoid douching, as it can disrupt the pH balance of your vagina and lead to infection.
- Change your underwear regularly and wash them using hot water.
The most common condition is vaginal thrush, caused by a mismatch of the vaginal fungi that are already present naturally, primarily Candida albicans. A healthy pH level, beneficial bacteria called lactobacilli, and a strong immune system help keep Candida under control.