Perhaps the most common and popular pain relief method adopted by woman opting for hospital births, Epidural anesthesia
What is means by an Epidural Anesthesia and when is it recommended?
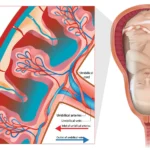
A popular pain relief method, Epidural anesthesia helps block the impulses from nerves in the lower spinal region. The resulting decreased sensations from the medication help remove the pain associated with labor during childbirth.
Administering an epidural
The epidural injection is always administered in the back while the patient is either lying on the left side or in a sitting position. A carefully placed catheter in the epidural space near the lower part of the spinal cord is used for administering the medication, hence the name epidural.
The two types of epidurals popular today are the Regular and the Combined Spinal Epidural (CSE). The former method helps reduce some of the side effects of anesthesia, allowing the mother to be conscious and participate in the delivery process. The later reduces muscle strength, reaction time and balance, providing four to eight hours of relief from pain.

Benefits of Opting for an Epidural during Delivery
The epidural is helpful for women during delivery. It not only helps the patient deal with fatigue, discomfort, and exhaustion but also helps the patient relax and have more positive and participative childbirth. The medication administered also gives some degree of relief from pains during the recovery phase following delivery. Although the majority of the women are in agreement regarding the relaxative properties of the medication; the overall experiences of a few women who chose to undergo epidural anesthesia does show some variances. These variances can be attributed to the skill of the person administering the medication i.e. the anesthetist.
Side effects of having Epidural Anesthesia
The side effect on mother and baby due to the administration of epidural anesthesia varies according to medication used, its dosage and duration of administration of medication.
- Since epidurals are a combination of anesthesia and narcotics, there is a probability of a sudden drop in blood pressure which may require to be treated with oxygen, IV fluids, medications or a combination of the three. Blood pressure is therefore continuously monitored to ensure that the baby is not affected by insufficient blood supply.
- A continuous tab is kept on fetal heart rate. The expectant mother is also made to change position frequently as lying in a single position can slow down labor.
- Nausea, shivering, backache, shivering, ringing of the ears, difficulty while urinating and soreness at the point of needle insertion are normally experienced after administration of an epidural anesthetic.
- Pushing is more difficult after administration of an epidural which slows down the labor. Often medical intervention like inducing labor by subsequent administration of Pitocin, vacuum extraction or cesarean may become necessary based on mother’s and baby’s health.
- The probability of longer labor.
- Numbness due to the epidural injections may result in an inability to walk without assistance for a few hours following childbirth.
- A possibility of urinary incontinence post-partum.
- The probability of fever is high.
- Collection of fluids (edema) in the breasts making it difficult for the baby to latch on and nurse.
- Lower milk production in mother’s body due to incorrect and insufficient sucking by the baby.
The effect of using epidural anesthesia during childbirth varies for each individual case. The expectant parents should make an informed decision after weighing the benefits and associated risks for both the mother and the baby.