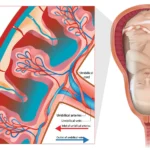
During pregnancy, a woman’s body is more prone to get bladder or urinary tract infection. We all know that progesterone levels will increase during pregnancy, which keeps a woman’s body at risk of bladder infection. If you suspect that you have a bladder infection, it is most important to get a diagnosis and proper treatment else untreated bladder infection can lead to various pregnancy complications.
Symptoms that indicate you have bladder infection:
Bladder infection may cause you to urinate more frequently than you normally do. Sometimes you may notice even blood in the urine. Urine comes out with a strong odor. Some other symptoms that you experience include:
- Cloudy urine
- Lower abdominal pain
- Pelvic discomfort
- Pain or burning sensation while urinating
Effects of an untreated bladder infection on your pregnancy:
If bladder infection left untreated, it can lead to premature delivery, premature labor, low birth weight, and perinatal mortality. A study conducted on more than 50,000 pregnancies, it was showed that women with bladder infection had a greater risk of perinatal mortality.

Sometimes, bladder infections may not present any symptoms, so it makes more difficult for diagnosis. So, pregnant women are suggested to undergo urine culture between 12-16 weeks of pregnancy to determine any existence of bacteria. It the test show bacteria in the urine, pregnant women are prescribed with antibiotics that are safe to use.
Treating bladder infection during pregnancy:
Pregnant women who are diagnosed with a bladder infection should get proper treatment to reduce the risk of premature delivery and various other risks like high blood pressure.
When you are prescribed with antibiotics, you have to consider various factors like:
- The effectiveness of the drug
- Pregnant woman’s health
- Stage of the pregnancy
- Possible effects on the growing baby
Preventing bladder infection from occurring:
One of the best ways to avoid bladder and urinary tract infection is NOT to ignore the urge to urinate.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Urinate immediately after the intercourse.
- Try to avoid usage of sprays, powders, and soaps at the genital area.
- Use cotton underwear only.
- Avoid wearing pantyhose for longer periods.
- Avoid taking over-the-counter drugs that dry up secretions.