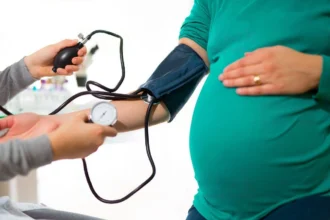
Pitocin – A labour-inducing medication. Know its benefits, risks, and complications
The injection known as Pitocin is a synthetic version of the hormone oxytocin. A hormone known as oxytocin is responsible for the contraction of the uterus. It is administered during labor through an intravenous (IV) line to induce or speed up contractions. Pitocin will be discussed in this article, including its use, potential side effects, and difficulties. Purpose To start…
When does the baby bump start to show during pregnancy?
Every pregnancy is distinct from the others. The baby bump start showing in the first trimester. While, for some other women, it may appear in their second trimester. Generally, most women's belly bumps start to show at the end of the first trimester or the beginning of the second trimester. Although your body changes rapidly in the first trimester, you…
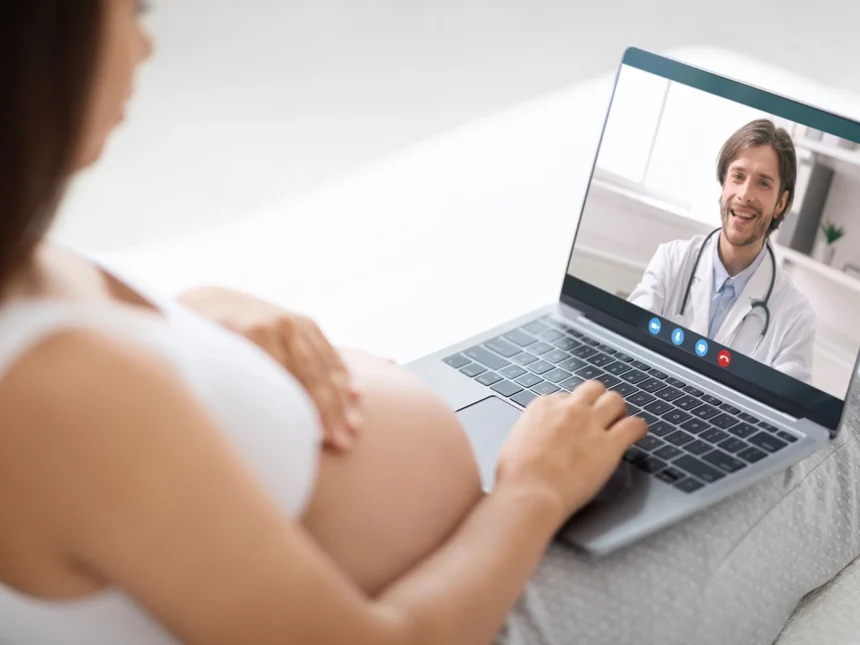
How Telehealth Medical services can Improve Maternity and Prenatal Care
Telehealth Medical services
Latest Articles From Moms Womb
How Telehealth Medical services can Improve Maternity and Prenatal Care
Pregnant patients can receive life-saving medical care through telehealth medical services. Few patients in rural…
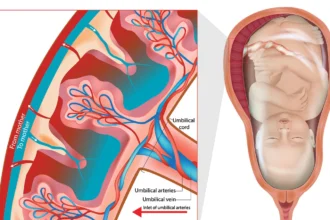
All you need to know about Placental Insufficiency
When a woman becomes pregnant, a new organ known as the placenta begins to form…
Melasma During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
When you have a newborn, you have a lot going on. During your first trimester…
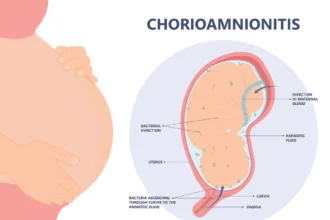
What Is Chorioamnionitis? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
Chorioamnionitis is a bacterial infection that may take place either before or while labor is…
Pitocin – A labour-inducing medication. Know its benefits, risks, and complications
The injection known as Pitocin is a synthetic version of the hormone oxytocin. A hormone…
Gearing Up for Pregnancy- Know Real Benefits of Preconception Care
"Life's Biggest Miracle is the Gift of Having Life Growing Inside of You." It's important…
What is RPL and their Causative Factors?
RPL is the short form of repeated pregnancy loss. This illness causes unquantifiable emotional trauma…
Care Guidelines During Hypertension in Pregnancy
Hypertension in pregnancy, few women may experience high blood pressure, which could put both the…
Fruits that lead to miscarriage during six months of pregnancy
Being a mom is a fantastic feeling; it all starts with pregnancy. Consumption of certain…
What Are The Signs Of Two-Month Pregnancy?
Are you pregnant? Symptoms of a two-month pregnancy Many new mothers are unaware of it.…
10 Indisputable Myths on Abortion
"I've noticed that everybody who is for abortion has already been born." Lots of myths…
Whether having Multiple Abortions is Safer?
Do several abortions, for example, make one safer? One of the myths surrounding abortion is…
Discover Categories

Pregnancy Symptoms
51 Articles
Pregnancy Complications
87 Articles
Pregnancy Tips
46 Articles
Pregnancy Health
117 Articles-
Discover More of What Matters to You:
- Abortion
- Fertility Treatment
- Breast Feeding
- Ovulation
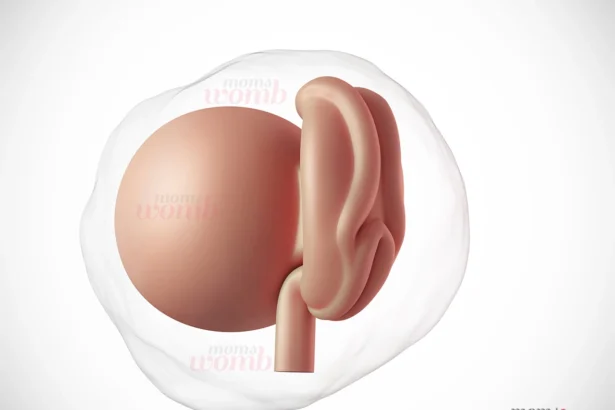
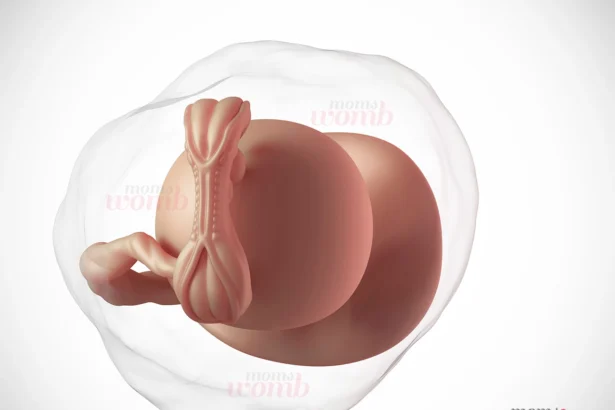
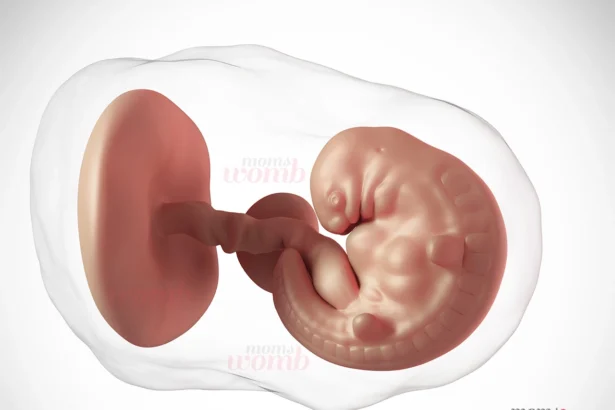
Baby Development Month by Month in the Womb
Are you excited to know how baby development occurs every month during your 40-week pregnancy period? Let’s take a look at what is happening inside your womb during pregnancy. Month…
What Are The Signs Of Two-Month Pregnancy?
Are you pregnant? Symptoms of a two-month pregnancy Many new mothers are…
How does the stomach feel when you’re pregnant for the first time?
Your stomach may feel different during first time pregnant symptoms. When the…
All you need to know about Placental Insufficiency
When a woman becomes pregnant, a new organ known as the placenta…
Melasma During Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
When you have a newborn, you have a lot going on. During…
Latest Articles
Vomiting bile in eight months of pregnancy. Should you worry?
The yellow liquid you vomit is your stomach juice. So vomiting yellow…
How does the stomach feel when you’re pregnant for the first time?
Your stomach may feel different during first time pregnant symptoms. When the…
Miscarriage on Pregnancy, At 6 Weeks: Symptoms & Causes
Miscarriage on pregnancy is very common. There are a few common pregnancy…
Pregnancy Baby Development During Third Month
During pregnancy, baby development phase, the next, and likewise, the first three…
30 Weeks Of Pregnancy: Baby Development
During your 30 weeks of pregnancy, your baby is still developing, while…
What Kind of Breast Pain Indicates Pregnancy?
"Life's biggest Miracle is the Gift of having Life Growing Inside of…
Can You Get Pregnant From Precum During Ovulation?
Are you wondering whether there are real chances of getting pregnant from…
Is Abortion Pill Reversal Conceivable?
Abortion pill reversal- A few women may reconsider having an abortion after…
InfoGraphics & Videos